Down in Front
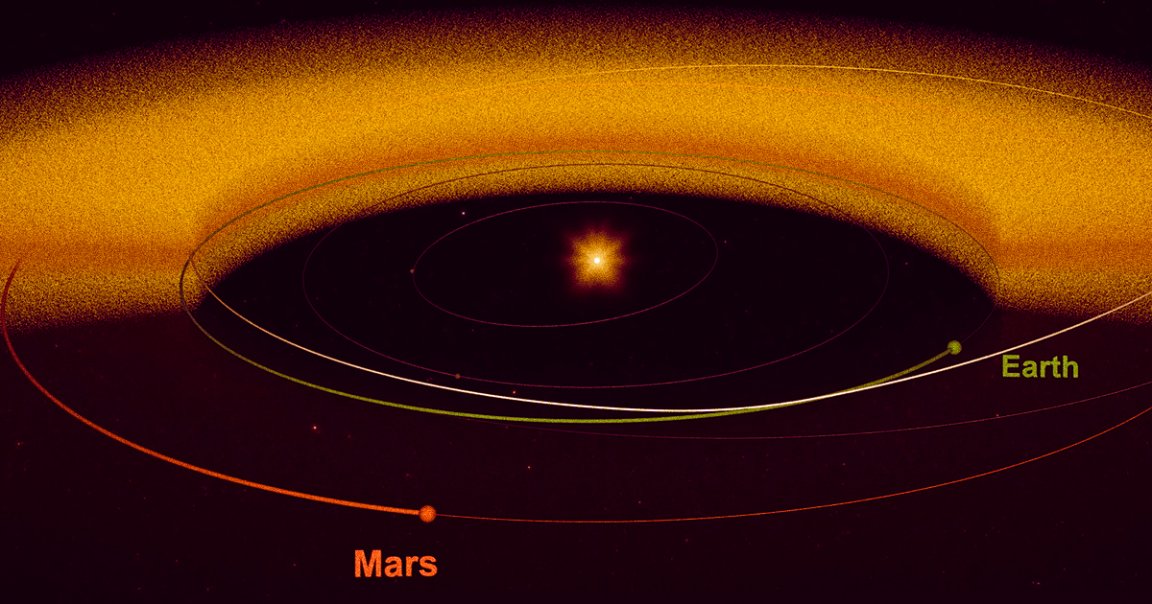
NASA’s Juno spacecraft accidentally uncovered a bizarre phenomenon as it flew to Jupiter: clouds of fast-moving dust, blowing away from Mars, are bombarding the entire inner solar system — including Earth.
NASA scientists first took notice when streams of particles, which they originally mistook for leaking fuel, blocked Juno’s star-charting cameras, according to a NASA press release. It turns out that the unusual trails were actually pieces of Juno itself alongside the Martian dust, whipping throughout the inner solar system, that chipped them away. The hazardous discovery, aside from being an unusual act of interplanetary aggression, could help NASA and other agencies chart safer courses through the solar system.
War of the Worlds
Scientists already knew that there were clouds of dust orbiting the Sun, but they assumed that they stemmed from distant asteroids or comets and gradually made their way into the inner solar system.
But NASA’s research, published Tuesday in The Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, used Juno’s cameras to track the distribution and trajectory of the dust clouds and revealed that the culprit is actually Mars. And there’s so much of the dust, the scientists found, that it even makes its way to Earth’s atmosphere.
A new NASA video describes the finding:

Chipping Away
Thankfully, Juno and its solar panels are fine, despite the dust chipping away at them as it bombards the spacecraft at extremely high speeds.
Juno, serving as a proverbial canary, could help keep future spacecraft safe now that NASA better understands these cosmic dusts and where they’re coming from. The tiny particles can still pack a serious punch, so space agencies will likely try to use this research to avoid them altogether the next time they launch a mission.
READ MORE: Serendipitous Juno Spacecraft Detections Shatter Ideas About Origin of Zodiacal Light [NASA]
More on Mars dust: NASA Suggests Giant Dust Storms Blew Mars’ Water Into Space