

Hindsight is a wonderful thing. Looking back from what we know now, the idea of a steady state universe seems like a model that doesn’t fit with our understanding of cosmology. As I said, hindsight is a wonderful thing! At the moment, the Big Bang model is what we consider to be the best fit model for explaining the deep past of the universe but over the decades there have been several others proposed — some that were better than others. The steady state universe was one of those theories proposed.
The steady state model was proposed by three individuals in 1948, Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold and Fred Hoyle. It is based on the assumption that on the large scales the universe is completely homogenous; that it looks the same from anywhere in the universe at any given time. At the time, this theory wasn’t quite as crazy due to our lack of understanding of the universe. The more that we’ve learned about the universe over the past half century, the more likely that the steady state universe theory is just plain wrong.
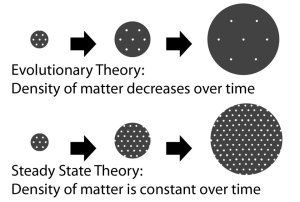
The idea of the steady state model was to account for some of the problems that were considered from the Big Bang model: the fact that the universe was calculated to being younger than the solar system was a big problem with the Big Bang model in 1948. The issue back then was that the cosmological constant was much, much higher back in 1948 than what it has been calculated now, the very recent Planck mission getting ~67 km/s/Mpc or the ~72 km/s/Mpc from the WMAP mission data. The very original cosmological constant was calculated by Hubble to be on the order of 500 km/s/Mpc, even after more accurate results had been taken. In 1948, it was still MUCH higher than what we know to be true today. Like several of the other theories that were considered at the time, the steady state model actually fixed some issues with the Big Bang model of the time.
There were a few reasons why the steady state model was eventually discontinued, and one of the reasons was not scientific at all, but purely philosophical. The idea of having a universe that always existed didn’t sit too well with many people as it went against creationist beliefs; that the universe had no beginning and always existed. Although this isn’t suggesting that the church was beating down on scientists like they did in centuries earlier, this was just a feeling amongst the different scientists.
Apart from the philosophical reasons, there were plenty of other scientific reasons for believing that the Big Bang model wins over that of the steady state model. As the steady state model suggested that the universe was homogenous (the same when viewed from every direction and any point in time within the history of the universe), observations of the earlier parts of the universe go against this. From our perspective, the universe is isotropic on large scales, as in, it looks the same no matter what direction we look, but the accelerating expanding universe doesn’t allow for it to be homogenous. To keep a universe homogenous it needs to have a constant density, and with the universe expanding, this means that under the steady state model matter is being created as new space is formed.
The last comment means that there should be both old and new galaxies together at the same time, but this is not what we observe when we look out into the universe. The Big Bang model states that in the early parts of the universe, the density was much higher, whereas the steady state model means that the universe today should look more or less identical to what it did 13 billion years ago — it has always looked the same and will always continue to remain the same.
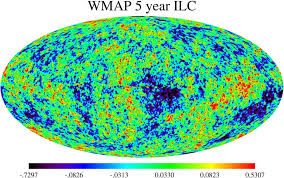
Another proof against the steady state universe is the detection of microwaves from all directions. According to the steady state model, this is caused by ancient stars having their light absorbed and scattered by dust and what not. Obviously, if it was point-like objects that are being scattered then the microwave data that was collected wouldn’t have been anywhere near as smooth as what it is. Having a look at the WMAP data we have or even the Planck data, the variance cannot have come from point-like sources such as stars.
Throughout history, many different theories have been proposed to explain different phenomenon, some far more outlandish than others. The steady state model was just one of the many theories that have been proposed in the last century to explain where the universe came from and where it is heading. Looking back with the information we know now, it can sometimes be hard to believe that theoretical models such as these could have ever been thought of, as they’re so far from the truth. To put this into practice for what we know now, string theory is a great example. String theory is a way in which many scientists are trying to unify general relativity and quantum mechanics, and in a few decades, we may all either be looking back at string theory as being the hard truth, or some crazy idea and exclaiming “What on Earth were they thinking!”