
One Smart Bot
If imitation is the sincerest form of flattery, OpenAI’s newest robot system should leave humanity blushing. Not only can it successfully replicate human behaviors, it can do so after just a single demonstration of the task.
The research company co-founded and chaired by Elon Musk used two separate neural networks to develop its one-shot imitation learning system.
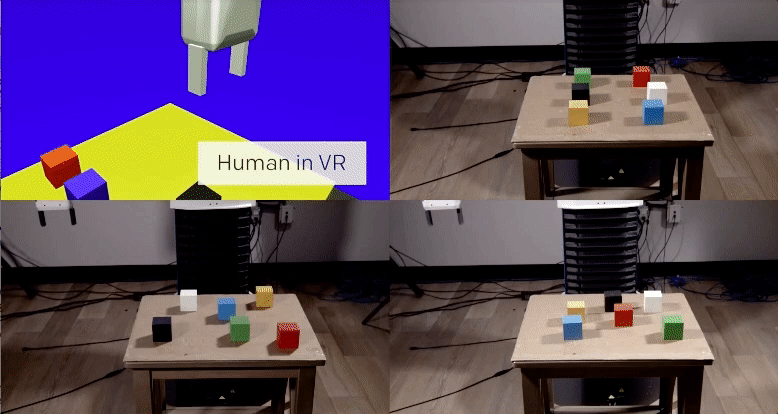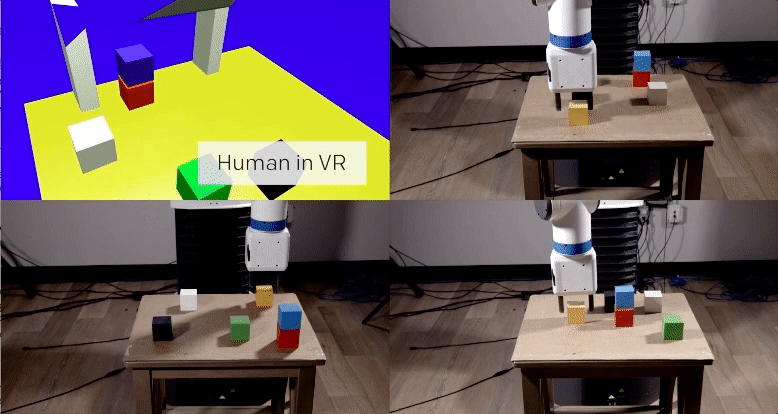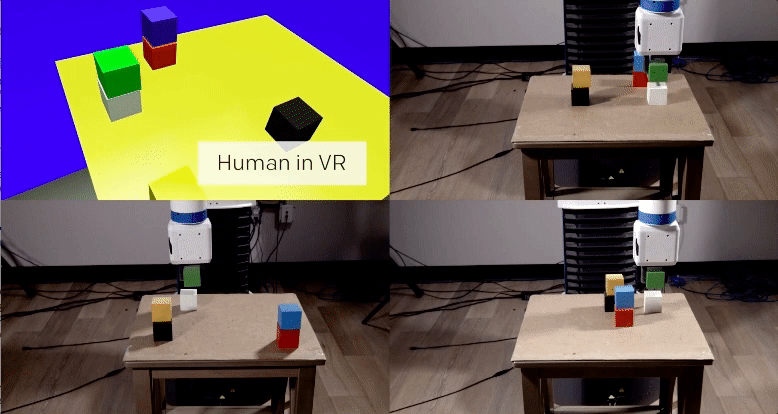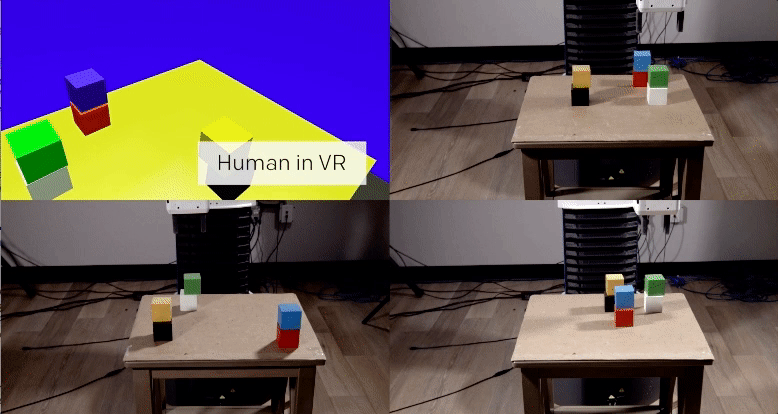
The first, a vision network, analyzes an image from the robot’s camera to determine the location of objects in reality (in OpenAI’s video example, these objects are blocks of wood on a table). The network is able to do this despite never having seen the actual table or blocks before. Instead, the researchers trained it using hundreds of thousands of simulated images, each featuring various permutations of lighting, textures, and objects.
The second, an imitation network, determines the intent of a task it observes a human demonstrating via a virtual simulation. It then imitates the task in the real-world setting. Again, this network was trained on thousands of virtual demonstrations, but none that took place in reality.
By the time the system was called upon to imitate a simulated demonstration in reality, it could do so after viewing the demonstration only once. Even more remarkably, the system was able to complete the task even if the starting parameters didn’t quite match up. For example, the blocks didn’t need to be in the exact same location as the demonstration for the system to know how to stack them. If a blue block went on top of a white block in the demonstration, the system replicated that task, even if the starting locations of the blocks wasn’t identical.
New Ways of Learning
Unlike Musk’s numerous other endeavors, OpenAI is a non-profit. Its purpose isn’t to make money, but to support and guide AI innovation. To that end, it’s already quite successful.
In December, the company launched Universe, an open source platform where users could measure and train their AI using games, web browsers, and various software. Essentially, the platform gives AI the ability to replicate how humans use computers, which allows developers to train their systems to complete any computer-based tasks humans can do.
This week, OpenAI followed that up with Roboschool, open-source software for robot simulation. It features a dozen environments in which users can test their robots, and it’s integrated with OpenAI Gym, a toolkit that gives developers the ability to give and receive feedback on their work, providing them with an online community to support development in AI.
Beyond OpenAI, researchers are already finding ways to teach robots to do everything from read to dream. They’ve created AI systems that can learn on their own and even ones that can teach each other. Education is being reinvented from the ground up to meet the needs of this new technology, and as our mechanical counterparts get smarter, our lives will get easier, safer, and maybe even a little more entertaining.