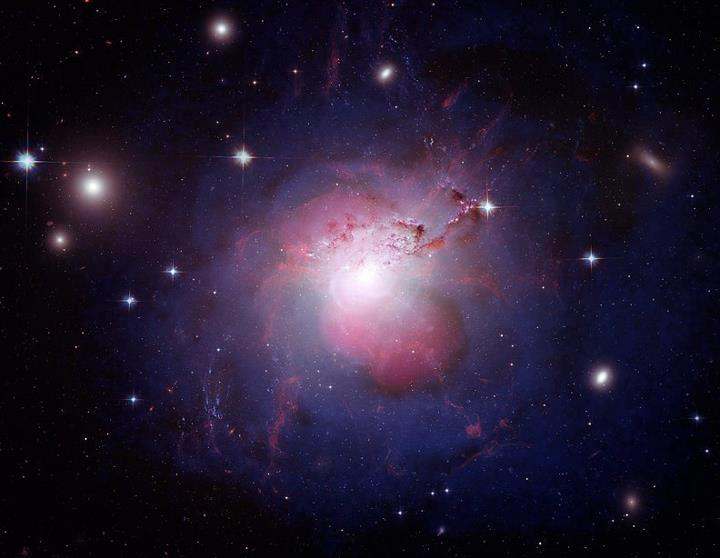

This bright, almost brain-shaped region is Perseus A (otherwise known as NGC 1275), a galaxy seen in visible light collected by the Hubble Space Telescope. Lurking more than 237-million light-years away from Earth (in the constellation of Pegasus), Perseus A — a Seyfert galaxy — is, not surprisingly, a member of the Perseus Galaxy Cluster
In addition to its classification (Seyfert galaxies are always bright and very active), this galaxy is laced with filamentary structures, which are impressively highlighted in this composite. X-ray data comes from Chandra Observatory, with the radio data acquired by the Very Large Array. This, with the visible light data from Hubble, help paint a clear picture of the underlying magnetic structure that keeps these filaments in place. Speaking of the filaments, they vary in size drastically. Some of them span just 200 light-years across, while others extend more than 200,000 light-years in diameter.