Stellar Fusion
For the first time, scientists were able to directly measure the sort of nuclear fusion happening at the Sun’s core.
The study, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, reveals that our star performs what’s called the carbon-nitrogen-oxygen (CNO) fusion cycle, a process that involves heavier elements than what scientists expected for a star of the Sun’s size. Most importantly, it confirms empirically that the CNO cycle exists, something scientists haven’t been able to do since hypothesizing it during the 1930s.
Wide Net
Past attempts to study the Sun’s fusion led to mismatched data from indirect sources, according to a University of Massachusetts Amherst press release. This new study, however, went straight to the source by capturing neutrinos: extremely-elusive subatomic particles called neutrinos that are constantly fired off by the Sun’s core but usually pass straight through the Earth.
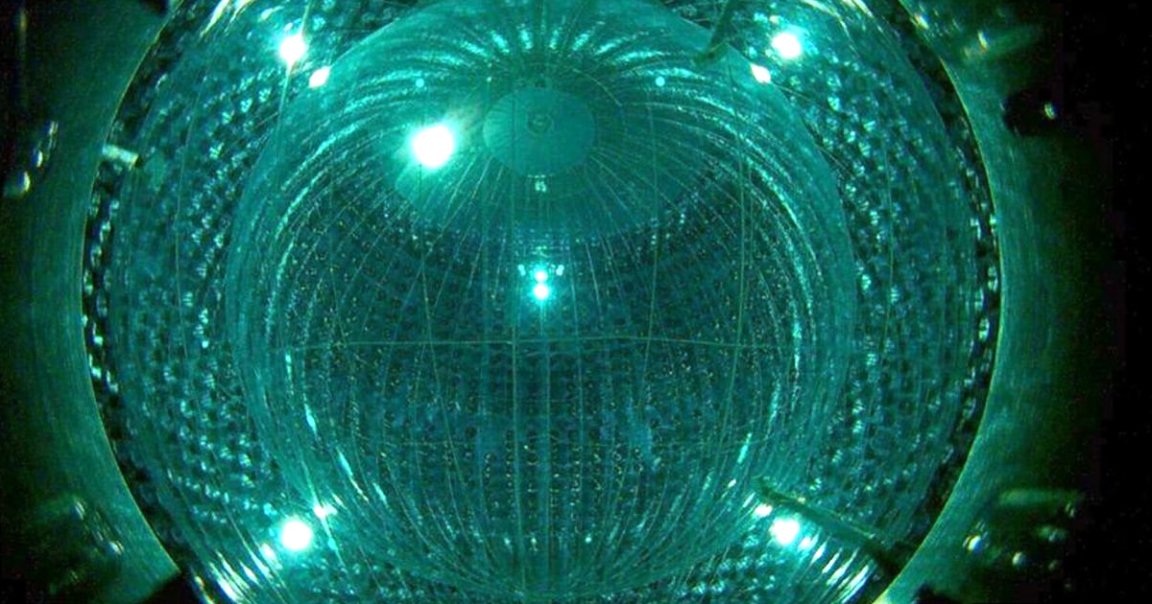
Using the Borexino detector, an underground facility in Italy, a team of over 100 scientists managed to spot these CNO neutrinos coming from the Sun — something scientists assumed would only happen with much larger stars that contain heavier elements.
New Life
Scientists had already found neutrinos given off when the Sun fuses hydrogen into helium, a hallmark process of lighter stars that gives off 99 percent of the sun’s energy. The new discovery not only extended the lifespan of the Borexino detector — which was scheduled to be decommissioned next month — but also revitalized scientists’ understanding of the cosmos.
“Confirmation of CNO burning in our sun, where it operates at only one percent, reinforces our confidence that we understand how stars work,” UMass Amherst physicist Andrea Pocar said in the release.
READ MORE: Neutrinos yield first experimental evidence of catalyzed fusion dominant in many stars [University of Massachusetts Amherst]
More on fusion: Studying the Sun’s Atmosphere Could Make Fusion Power a Reality