In Disarray
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) may have to wait on certain essentials, because a resupplying cargo ship has hit an unexpected snag.
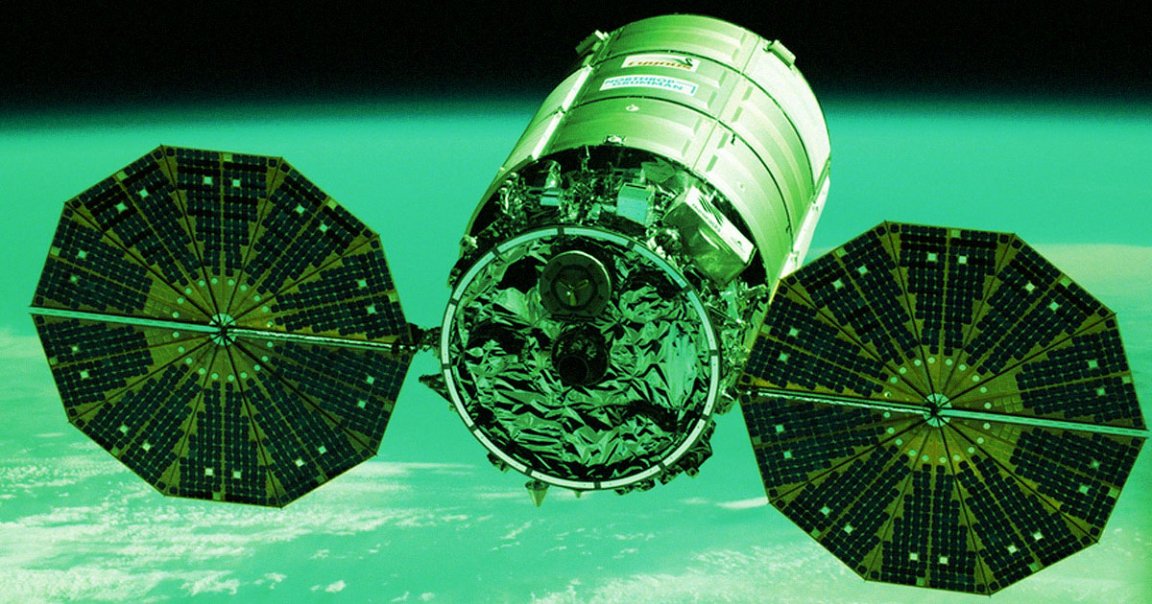
The NG-18 Cygnus cargo spacecraft, built by Northrop Grumman, is loaded with four tons worth of supplies including food, research equipment, and other hardware. Its launch on Monday morning from Virginia went as smoothly as one could hope, but after parting ways from the rocket it hitched a ride on, its journey to the ISS hit an unexpected snag.
Specifically, one of the two solar arrays that help power the spacecraft failed to unfurl and deploy. As of now, according to a brief NASA update, “Northrop Grumman is gathering data on the second array deployment and is working closely with NASA.”
Still, Northrop Grumman remains optimistic that the Cygnus spacecraft can complete its journey with what power is left — and even remain on schedule.
“Northrop Grumman has reported to NASA that Cygnus has sufficient power to rendezvous with the International Space Station on Wednesday, Nov. 9, to complete its primary mission, and NASA is assessing this and the configuration required for capture and berthing,” NASA said.
The Expendable
The NG-18 Cygnus is one of — as the name suggests — 18 built and deployed in the last decade to resupply the ISS, which is also resupplied by SpaceX’s Dragon capsule and Russia’s Progress spacecraft. This current iteration has been named the SS Sally Ride after the first American woman in space.
Like Russia’s Progress, a Cygnus spacecraft does not return to Earth — at least, not in one piece. Instead, they’re intended to be expendable. After berthing with the ISS via a robotic arm and dropping off its cargo, astronauts load the Cygnus up with trash. Then the poor freighter is banished to Earth’s atmosphere, where it burns up upon re-entering.
So if anything, the hiccup in its journey to the ISS may have bought the brave spacecraft just a little more time to enjoy the world before it’s doomed to incineration.
More on spacecraft: NASA Just Shot Tiny Bullets at Its Mars Spacecraft